Proof-of-concept (PoC) of exploits for known vulnerabilities are widely shared in the security community. They help security analysts to learn from each other and they facilitate security assessments and red teaming tasks.
But not all PoCs are trustworthy!
Researchers at Leiden University released a paper showing that cybercriminals are trying to install malware on security researcher systems via fake Proof-of-Concepts (PoC).
If you are a security professional beware of fake PoCs from public code repositories like GitHub!

Research revealed malicious repositories targeting security professionals
Thousands of malicious repositories were found in an investigation that lasted between 2017 and 2021 from GitHub repositories sharing PoCs.
More than 10% of the total investigated repositories (4893 out of 47313) were qualified as malicious.
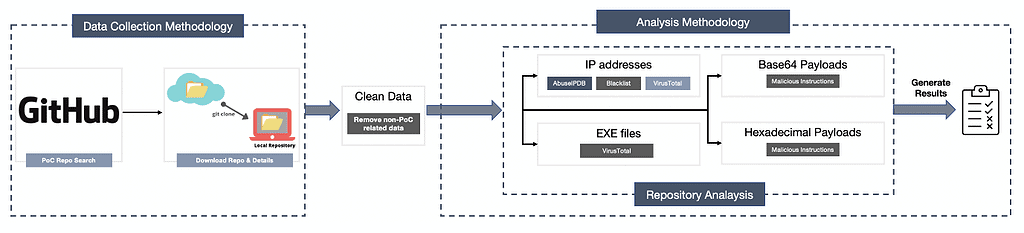
The identification methods
A big challenge for the researchers was to find reliable indicators of a malicious PoC.
The proof of concepts are usually developed by hackers or security professionals with the end-goal to compromise a system by exploiting a vulnerability in a specific product. Thus, these PoCs represent by design malicious software that would be flagged by security systems designed to detect exploits.
So, the researchers had to identify properties that indicate some other malicious goals, unrelated to the original PoC goals.
They did this by looking for the following indicators:
- IP addresses: The researchers extracted IP addresses and removed all private IP addresses. The results were compared with VirusTotal, AbuseIPDB, and other publicly available blocklists.
- Binaries focused on EXE files that can be run on Windows systems since most of the malware attacks are conducted against Windows users. After extracting them, the researchers checked their hashes in VirusTotal and from those detected as malicious, dismissed the ones listed as an exploit of the target vulnerability.
- Obfuscated payloads: By performing hexadecimal and base64 analysis, the researchers were able to extract some extra malicious PoCs.
Conclusion
This research shows that attackers are targeting security professionals by trying to plant malware on their systems or open backdoors to them and at the same time open the possibility of attacks on customers of the security companies utilizing those PoCs.
Dimitris is an Information Technology and Cybersecurity professional with more than 20 years of experience in designing, building and maintaining efficient and secure IT infrastructures.
Among others, he is a certified: CISSP, CISA, CISM, ITIL, COBIT and PRINCE2, but his wide set of knowledge and technical management capabilities go beyond these certifications. He likes acquiring new skills on penetration testing, cloud technologies, virtualization, network security, IoT and many more.