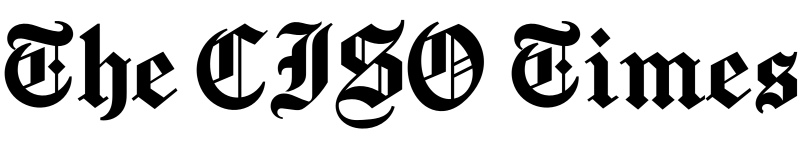34 Russian-speaking groups distributing info-stealing malware under the stealer-as-a-service model, were identified by Group-IB.
In the first seven months of 2022, the gangs collectively infected over 890,000 user devices and stole over 50 million passwords.
In 2022, info-stealing malware has grown into one of the most serious digital threats.
Racoon and Redline Information Stealers
The cybercriminals use mainly Racoon and Redline stealers to obtain passwords for gaming accounts on Steam and Roblox, credentials for Amazon and PayPal, as well as users’ payment records and crypto wallet information.
Note that the attackers responsible for the most recent attack on Uber purchased the credentials compromised with the Racoon stealer.
What are Information Stealers?
An info stealer is a type of malware that collects credentials stored in browsers (including gaming accounts, email services, and social media), bank card details, and crypto wallet information from infected computers, and then send all this data to the malware operator.
After a successful attack, the scammers either obtain money themselves using the stolen data, or sell the stolen information in the cybercriminal underground.
Devices Infected and Information Stolen
All Cybercrime groups orchestrated their attacks via Russian-language Telegram groups.
Group-IB estimates that between March 1 (when Group-IB started researching the scheme) and December 31, 2021, stealers operated via Telegram groups were able to compromise 538,000 devices. In the first 7 months of 2022, they were found to be almost twice more active infecting more than 890,000 devices in 111 countries.
The top 5 most often attacked countries in 2022 were the United States, Brazil, India, Germany, and Indonesia with 91,565, 86,043, 53,988, 40,750, and 35,345 infected devices respectively.
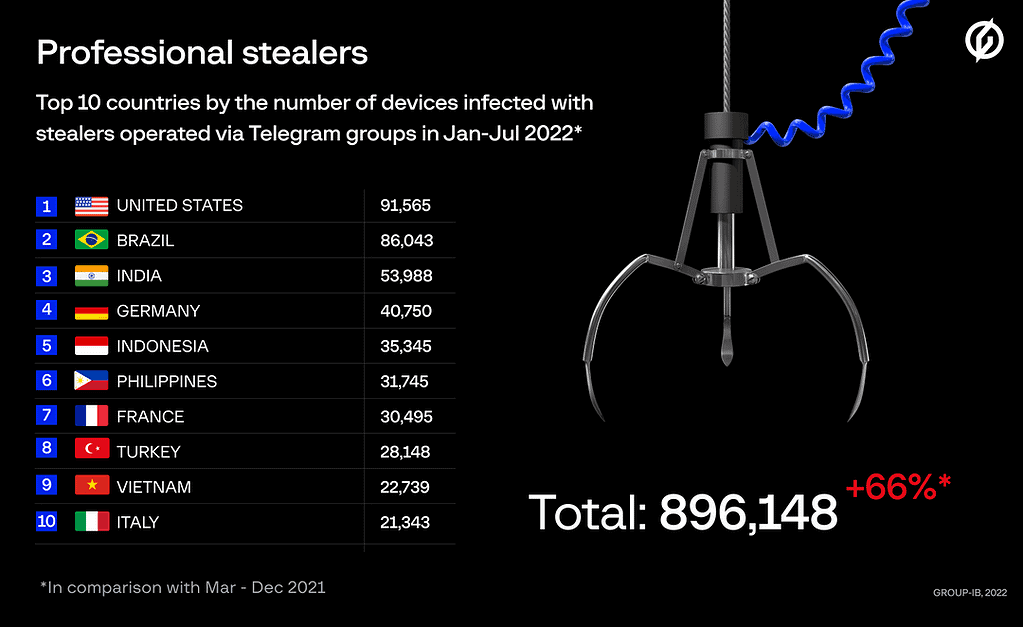
According to the analysis of Telegram groups, for the last 10 months of 2021 cybercriminals collected 27,875,879 sets of passwords, 1,215,532,572 cookie files, 56,779 sets of payment records, and data from 35,791 crypto wallets.
In the first 7 months of 2022, threat actors stole 50,352,518 passwords, 2,117,626,523 cookie files, details of 103,150 bank cards, and data from 113,204 crypto wallets. The underground market value of just the stolen logs and compromised card details is around $5.8 million, Group-IB experts estimate.
According to Group-IB, in 2021, threat actors worldwide most frequently collected PayPal account credentials (more than 25%) and Amazon credentials (more than 18%).
In 2022, the most targeted services are the same, namely PayPal (more than 16%) and Amazon (more than 13%). However, over the course of the year, cases of stealing passwords for gaming services (Steam, EpicGames, Roblox) in the logs have increased almost five-fold.
Dimitris is an Information Technology and Cybersecurity professional with more than 20 years of experience in designing, building and maintaining efficient and secure IT infrastructures.
Among others, he is a certified: CISSP, CISA, CISM, ITIL, COBIT and PRINCE2, but his wide set of knowledge and technical management capabilities go beyond these certifications. He likes acquiring new skills on penetration testing, cloud technologies, virtualization, network security, IoT and many more.