The recent LockBit ransomware attack on the Industrial & Commercial Bank of China (ICBC) marks a significant escalation in cyber vulnerabilities within the global financial sector. This event not only highlights the potential weaknesses in the cybersecurity defenses of major financial institutions but also underscores the far-reaching implications of such attacks on the stability of the global economy.
The Impact of LockBit on the U.S. Treasury Market
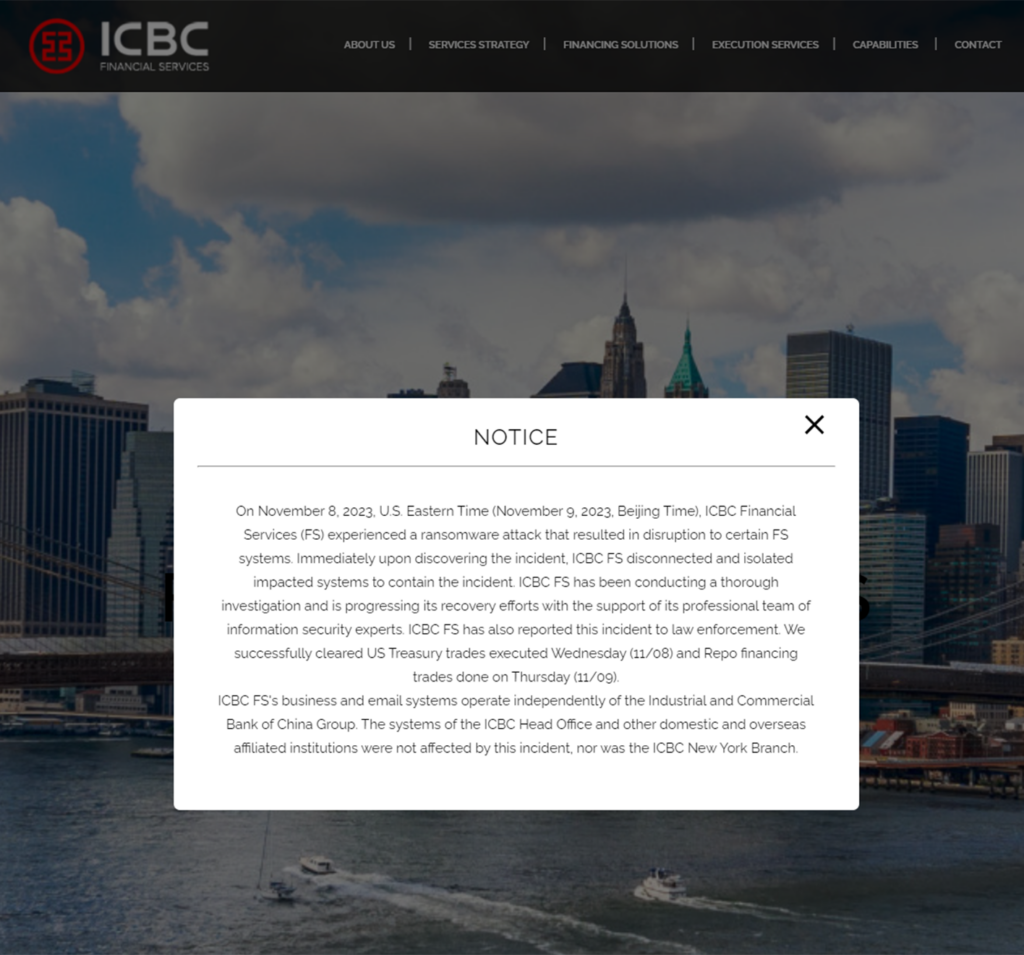
On November 8, the financial world was shaken by a ransomware breach at the American subsidiary of ICBC Ltd., a disruption that severely impacted U.S. Treasury trading operations. The LockBit ransomware group, known for its aggressive cyberattacks, claimed responsibility for this breach. With ICBC managing assets worth $5.7 trillion, this cyberattack sent ripples through the $26 trillion U.S. Treasury market, raising alarm bells over the security of global financial transactions.
Prepositioning: A Strategy for Future Cyberattacks?
A report by Resecurity, a Los Angeles-based cybersecurity firm, suggests that the LockBit attack on ICBC might be a strategic move to test the resilience of the global financial system against cyber threats. Termed as ‘prepositioning,’ this tactic aims to analyze the response mechanisms of financial institutions and the market’s reaction to such threats, potentially setting the stage for more significant cyberattacks in the future.
The Strategic Targeting of ICBC Financial Services
LockBit’s attack was strategically directed at ICBC Financial Services (ICBC FS), a crucial subsidiary of the state-owned lender. ICBC FS plays a pivotal role in international finance, offering global clearing, execution, and financing services to institutional clients. As reported by the Financial Times, this unit acts as an intermediary for entities such as governments, hedge funds, and traders in U.S. debt transactions.
Exploiting Vulnerabilities: The Role of Citrix NetScaler
The Treasury revealed that the LockBit attack exploited a known vulnerability in the Citrix NetScaler product suite. This breach temporarily hindered bank employees from accessing their corporate email and disrupted connections to the Depository Trust and Clearing Corporation, essential for resolving U.S. Treasury trades. Particularly affected were critical repurchase agreement (repo) transactions, underscoring the systemic importance of cybersecurity in the financial sector.
Conclusion: Strengthening Cybersecurity Defenses
The LockBit ransomware attack on ICBC is a stark reminder of the fragility of our global financial system in the face of evolving cyber threats. It emphasizes the need for robust cybersecurity measures and proactive threat detection strategies to safeguard financial institutions. As the landscape of cyber threats continues to evolve, the financial sector must remain vigilant and adaptive, ensuring the security and stability of global financial transactions.
Dimitris is an Information Technology and Cybersecurity professional with more than 20 years of experience in designing, building and maintaining efficient and secure IT infrastructures.
Among others, he is a certified: CISSP, CISA, CISM, ITIL, COBIT and PRINCE2, but his wide set of knowledge and technical management capabilities go beyond these certifications. He likes acquiring new skills on penetration testing, cloud technologies, virtualization, network security, IoT and many more.
