Researchers have recently sounded the alarm about a sophisticated and emerging form of voice phishing (vishing) called “Letscall.” This alarming technique is currently being used to target individuals in South Korea, posing a significant threat to their financial security and personal information.
Deceptive Tactics and Malicious Apps
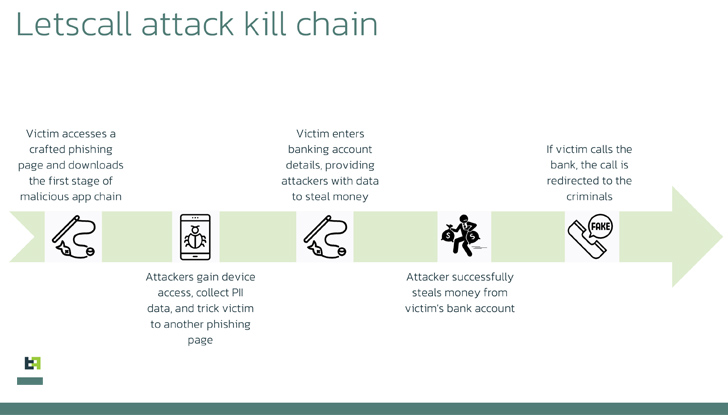
The criminals behind “Letscall” employ a complex, multi-step attack to trick victims into downloading malicious apps from a counterfeit Google Play Store website. These fraudulent applications serve as a gateway for the installation of harmful software, enabling the criminals to gain control over the victims’ devices.
Manipulation of Incoming Calls
Once the malicious software is successfully installed, it redirects incoming calls to a call center operated by the criminals. Skilled operators, pretending to be bank employees, then extract sensitive information from unsuspecting victims, further compounding the security risks.
Cutting-Edge Technologies and Evasion Techniques
To facilitate the rerouting of voice traffic, “Letscall” utilizes advanced technologies such as voice over IP (VOIP) and WebRTC. It also employs protocols like Session Traversal Utilities for NAT (STUN) and Traversal Using Relays around NAT (TURN), including Google STUN servers. These sophisticated techniques ensure high-quality phone or video calls and allow the attackers to bypass NAT and firewall restrictions.
The “Letscall” Group
The “Letscall” group consists of a diverse range of skilled individuals, including Android developers, designers, frontend and backend developers, and call operators specialized in voice social engineering attacks. This collaborative effort demonstrates the level of expertise and coordination employed by the criminals behind this malicious campaign.
Evasion Techniques and Manipulation of Commands
The malware operates in three stages, with the final stage involving the rerouting of incoming calls to the attackers’ call center. This stage incorporates specific commands, including Web socket commands, which manipulate the address book, create and remove contacts, and modify call filters. Such complex manipulation adds another layer of sophistication to the attack.
Exploiting Vulnerabilities
“Letscall” stands out due to its utilization of advanced evasion techniques. The malware incorporates Tencent Legu and Bangcle (SecShell) obfuscation during the initial download. In later stages, it employs complex naming structures in ZIP file directories and intentionally corrupts the manifest to confuse and bypass security systems, making it extremely challenging to detect and mitigate.
Fraudulent Activities and Financial Implications
Criminals have devised automated systems that call victims and play pre-recorded messages to deceive them further. By combining mobile phone infections with vishing techniques, these fraudsters can request micro-loans in the victims’ names, capitalizing on their confusion and redirecting calls to their centers. This leaves victims burdened with significant loans to repay, while financial institutions often underestimate the severity of these invasions, failing to address potential fraud.
Wider Implications and Potential for Expansion
Although the current threat is limited to South Korea, researchers caution that there are no technical barriers preventing these attackers from expanding their operations to other regions, including the European Union. This highlights the need for heightened awareness and proactive measures to prevent the spread of this sophisticated vishing attack.
Conclusion
The emergence of the “Letscall” vishing attack underscores the constant evolution of criminal tactics and their ability to exploit technology for malicious purposes. The group responsible for this malware demonstrates intricate knowledge of Android security and voice routing technologies, emphasizing the importance of robust security measures and vigilance in the face of emerging threats.
Dimitris is an Information Technology and Cybersecurity professional with more than 20 years of experience in designing, building and maintaining efficient and secure IT infrastructures.
Among others, he is a certified: CISSP, CISA, CISM, ITIL, COBIT and PRINCE2, but his wide set of knowledge and technical management capabilities go beyond these certifications. He likes acquiring new skills on penetration testing, cloud technologies, virtualization, network security, IoT and many more.
